Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour face’s hot spots may reveal how well you are aging
If facial heat maps prove effective at picking up signs of chronic diseases such as diabetes, they could become another health assessment tool.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists blamed migraines on cheese and chocolate
Exactly how migraines develop is still coming into focus, but scientists now know that many factors can trigger attacks.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s blood tests are getting better, but still have a ways to go
Blood biomarker tests could help doctors know if a person's cognitive symptoms are due to Alzheimer's or something else.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC has tightened rabies regulations for imported dogs. Here’s why
Dog rabies was eliminated in the United States in 2007. The new rules on bringing dogs into the country aim to keep it that way.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome ‘forever chemicals’ may be absorbed through our skin
PFAS, which are found in common products such as cosmetics, food packaging and waterproof gear, have been linked to health problems.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStopping cachexia at its source could reverse wasting from cancer
The immune protein interleukin-6 helps regulate body weight. Blocking it in the brain could restore appetite and muscle mass, a study in mice hints.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGetting drugs into the brain is hard. Maybe a parasite can do the job
Researchers want to harness the parasite that causes toxoplasmosis to ferry drugs, but some question if the risks can be eliminated.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new algae-based menstrual pad could stop leaks
By turning period blood into a gel, the pad’s alginate powder filler reduces leakage.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSepsis tests take days, putting patients at risk. A new method may cut wait time
A faster way to figure out what bacteria is causing a potentially deadly bloodstream infection could let doctors treat it more quickly and efficiently.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV prevention may only require two injections per year
There were no new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women taking a new PrEP formulation, a twice-yearly shot of the drug lenacapavir.
-
 Health & Medicine
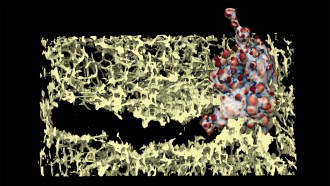
Health & MedicineSome melanoma cancer cells may punch their way through the body
A new study clarifies how melanoma cells use cell membrane protrusions called “blebs” to burrow through tissue.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow to stay healthy during the COVID-19 summertime surge
Infections peak in the summer and winter. Up-to-date vaccinations, testing and masking can slow the spread.